
Boron-Carbon Triple Bond Breakthrough – This World-First Miracle Redefines Chemistry Forever
| IN A NUTSHELL |
|
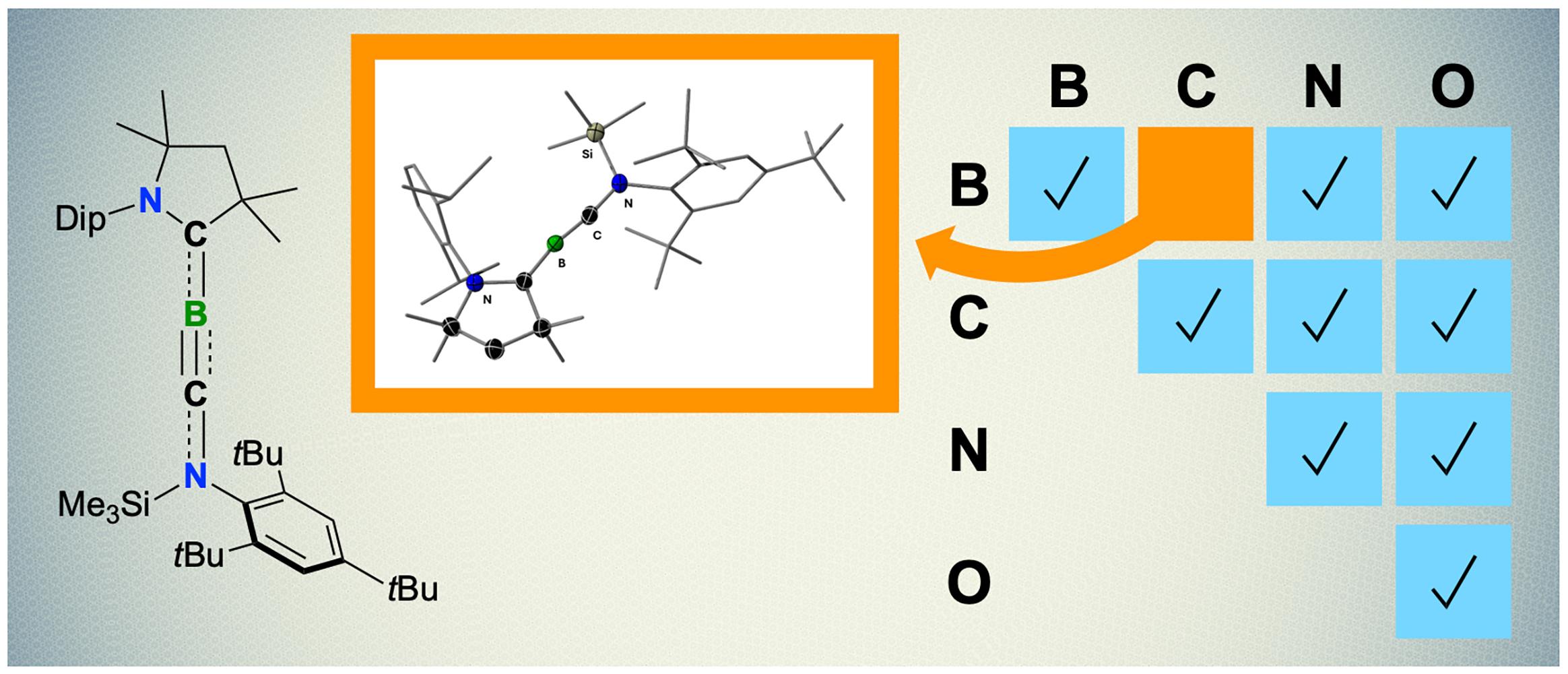
Breaking new ground in the realm of chemistry, researchers at the Julius Maximilian University of Wuerzburg in Germany have accomplished something previously thought impossible. They successfully synthesized a molecule featuring a boron-carbon triple bond. This breakthrough promises to reshape our understanding of chemical bonds and potentially revolutionize various fields. This feat was achieved under the guidance of Dr. Holger Braunschweig, marking a significant milestone in the study of chemical elements, specifically those positioned consecutively on the periodic table, such as boron, carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen.
The Elusive Boron-Carbon Triple Bond
The elements boron (B), carbon (C), nitrogen (N), and oxygen (O) are neighbors on the periodic table, boasting atomic numbers 5, 6, 7, and 8, respectively. While carbon, nitrogen, and oxygen are nonmetals, boron stands out as a metalloid. Despite these differences, these elements share the ability to form strong chemical bonds, including the much-coveted triple bonds. These bonds are foundational to the formation of molecules like carbon monoxide (CO) and atmospheric nitrogen (N₂), which plays a crucial role in Earth’s atmosphere.
However, a triple bond between boron and carbon remained elusive. Although stable double and triple bonds between two boron atoms or two carbon atoms were known, the boron-carbon triple bond was a missing piece of the puzzle. Dr. Holger Braunschweig and his team have finally synthesized this bond, creating a molecule known as boryne, which exists as an orange solid at room temperature. This achievement is a testament to the dedication and ingenuity of the researchers who have overcome significant challenges to make this discovery.
A Tough Spot for Boron
The creation of boryne was no small feat, as boron required “very special conditions” to form a triple bond with carbon. According to Rian Dewhurst, a senior scientist and co-author of the study, boron in this molecule is arranged linearly with carbon atoms. This arrangement creates a highly uncomfortable state for boron, necessitating unique experimental conditions for synthesis.
This discomfort is precisely what makes boryne so intriguing for researchers. The synthesized molecule’s structural properties were identified, and detailed studies on its reactivity were conducted. These investigations aim to unlock the secrets of boryne’s chemical behavior and explore its potential applications. The fact that such a bond has been realized underlines the innovative nature of the research team, pushing the boundaries of what is possible in the field of chemistry.
AI Outperforms Chinese Pilots in High-Stakes Aerial Combat: A Glimpse into the Future of Warfare
Investigating Boryne’s Reactivity
The reactivity of boryne is a focal point of the research. The chemists are eager to understand how its unique bonding structure influences its chemical interactions. Breakthroughs often arise unexpectedly, as evidenced by the discoveries of Teflon and superglue, both of which emerged from research with different original goals.
Maximilian Michel, a PhD student at the University of Wuerzburg and a key player in the molecule’s creation, highlights that compounds where individual atoms experience discomfort often exhibit fascinating reactivity. The team believes that their breakthrough could lead to new tools for chemical synthesis and provide deeper insights into the nature of chemical bonds and molecular structures. They hope to inspire other scientists to explore new possibilities, potentially leading to significant advances in chemical synthesis.
The Broader Impact of Basic Research
Dewhurst emphasizes that basic research like theirs inspires other researchers to venture into synthesizing compounds that may initially seem improbable. This spirit of innovation and exploration can lead to world-changing advances that emerge from seemingly “crazy ideas.”
The synthesis of the boron-carbon triple bond not only represents a significant achievement in chemistry but also underscores the importance of fundamental research. Such research fuels scientific progress, sparking new ideas and breakthroughs that can transform industries and improve our understanding of the natural world. As this discovery is published in the journal Nature Synthesis, it stands as a beacon for future research endeavors, inviting scientists to push the boundaries of what is possible and explore the uncharted territories of chemical synthesis.
With the successful synthesis of a boron-carbon triple bond, we are left to ponder: What new frontiers in chemistry and material science will this discovery open, and how will it shape the future of research and innovation?
Did you like it? 4.5/5 (22)









Wow, a boron-carbon triple bond? That’s mind-blowing! 😲